Preventive Maintenance and Repair
Preventive Maintenance and Repair
This guide recommends preventive maintenance and repair for various hydraulic tools, including hydraulic pumps, cylinders, pullers, shop presses, and hydraulic jacks. Regular maintenance ensures efficient operation, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of these tools. Each category includes key preventive maintenance steps and common repair suggestions.
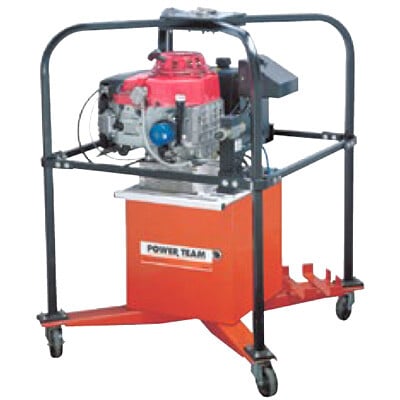

Hydraulic Pumps
Preventive Maintenance
- Check Fluid Levels: Ensure the hydraulic fluid is at the recommended level. Low fluid can lead to poor pump performance and overheating.
- Inspect for Leaks: Look for leaks around seals, hoses, and fittings. Leaks can indicate worn seals or loose connections.
- Fluid Quality: Regularly check the quality of hydraulic fluid. Replace it when it becomes contaminated or degraded (typically every 1,000 operating hours or per the manufacturer’s recommendations).
- Inspect Hoses and Connections: Ensure that hoses are not kinked, cracked, or worn. Check connections for tightness to avoid hydraulic fluid loss or contamination.
- Monitor Operating Temperature: Ensure the pump operates within the manufacturer’s recommended temperature range. Overheating can cause fluid breakdown and damage components.
- Check Relief Valve Settings: Ensure the pressure relief valve is properly set to avoid overpressure situations that could damage the pump or the hydraulic system.
Repair Recommendations
- Replace Worn Seals: Seals may degrade and cause leaks over time. Replace any damaged or worn seals to maintain pressure and fluid retention.
- Fix Hydraulic Leaks: Tighten loose fittings, replace damaged hoses, or replace faulty O-rings.
- Pump Motor Issues: If the motor is not running smoothly, inspect the electrical connections, check for wear on the motor, and replace the brushes (if required) or the motor if necessary.
- Relief Valve Malfunction: If the relief valve fails to release pressure or leaks, replace or clean the valve and adjust the pressure settings.
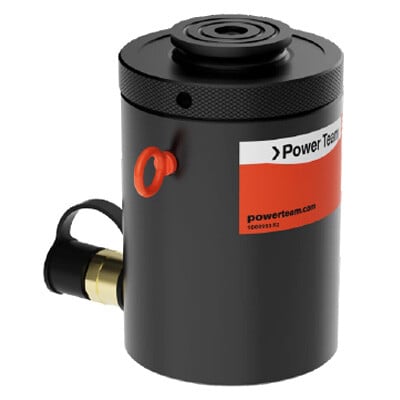

High-Pressure, Hydraulic Cylinders
Preventive Maintenance
- Check for Leaks: Inspect the cylinder rod and end caps for hydraulic fluid leaks, which can indicate a damaged seal or worn parts.
- Clean the Rod: Clean the cylinder rod regularly to prevent dirt and debris from entering the cylinder. Use a clean cloth and apply lubricant as necessary.
- Inspect the Rod for Damage: Check for nicks, scratches, or pitting on the rod surface, which can lead to premature seal failure.
- Lubricate the Piston and Rod: To reduce wear, ensure proper lubrication of moving parts, especially in high-load environments.
- Monitor Operating Pressure: Ensure the cylinder operates within its rated pressure range. Over-pressurization can cause internal damage.
- Inspect the Cylinder Mounting: Please ensure the mounting points are secure and there is no excessive play or misalignment.
- Cylinder Storage: keep in a clean, dry, indoor area, fully retracted, in a vertical position (piston rod down), away from extreme temperatures and direct sunlight, and with dust covers installed to prevent contamination; ideally, use designated storage racks or bins to maintain stability and prevent damage.
Repair Recommendations
- Seal Replacement: If the seals are leaking or damaged, replace them promptly. Pay close attention to the type of seal and its installation orientation.
- Rod Repair: If the cylinder rod is damaged (e.g., bent or corroded), repair or replace the rod to prevent further damage to the seals and the cylinder body.
- Cylinder Bore Damage: If the bore is scratched or scored, the cylinder may need to be honed or replaced.
- Replace Worn Pistons: If the piston is worn or damaged, replace it to ensure smooth operation and prevent further damage to the cylinder.
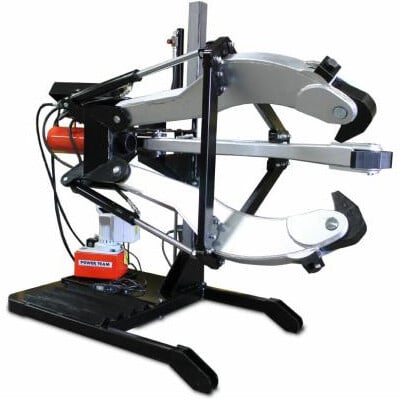

Hydraulic Pullers
Preventive Maintenance
- Check Hydraulic Fluid: Maintain proper fluid levels and check the fluid for contamination.
- Inspect for Leaks: Regularly check all hydraulic hoses, fittings, and connections for leaks.
- Clean the Puller: After each use, clean the puller thoroughly to prevent dirt or corrosion from building up on hydraulic components.
- Check Alignment: Ensure that all parts are properly aligned to prevent uneven forces or damage to the puller’s mechanism.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Lubricate threaded parts and moving components to reduce wear and prevent rust formation.
Repair Recommendations
- Seal and O-Ring Replacement: If leaks occur, inspect and replace seals or O-rings, which are typically the cause of hydraulic fluid loss.
- Check Hydraulic Hose Condition: Replace any cracked, kinked, or damaged hoses.
- Cylinder Damage: If the hydraulic cylinder is leaking or not holding pressure, inspect it for damaged seals or internal wear. Replace any worn components.
- Replace the Pulling Mechanism: If the jaws, bolts, or other mechanical components become bent or broken, replace them to avoid safety issues.
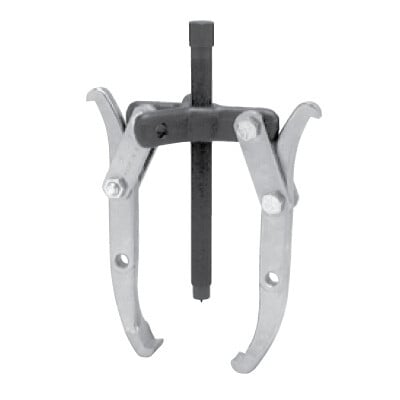

Mechanical Pullers
Preventive Maintenance
- Clean After Use: Always clean the puller thoroughly after each use. Use a clean rag or brush to remove dirt, grease, or debris from all components, especially threads and moving parts.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Regularly lubricate threaded rods, bolts, arms, and any moving parts with an appropriate grease or oil to prevent rust and ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect the Threads: Check the threads on the center bolt (or screw), arms, and other adjustable parts for wear or damage. Clean the threads regularly and lubricate them to prevent corrosion and to facilitate easy adjustments.
- Inspect the Jaws: Check the jaws of the puller for wear, cracks, or misalignment. Worn or damaged jaws can lead to poor grip and potentially damage the workpiece or the puller itself.
- Check the Center Bolt/Screw: The center bolt or screw is typically under high tension during use. Ensure it is straight and that the threads are intact. If the center bolt is deformed or damaged, it may not function properly and should be replaced.
Repair Recommendations
- Jaw Replacement: Replace damaged jaws with new ones. If the jaws are worn but not severely damaged, you may be able to grind or reprofile the tips, but this depends on the material and design of the puller.
- Center Bolt Inspection/Repair: Inspect the center bolt for visible wear or stripping. If the threads are stripped, replace the center bolt with a new one.
- Adjust Jaw Alignment: Check if the arms or jaws are properly aligned and have a firm grip on the workpiece. If the center screw is misaligned or damaged, replace it. Also, check the surface of the puller for any signs of wear that may cause slippage (such as worn threads).
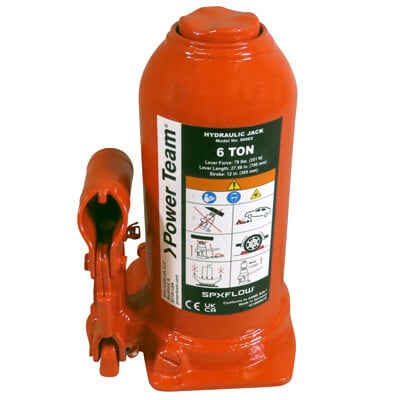

Hydraulic Bottle and Toe Jacks
Preventive Maintenance
- Check Fluid Levels: Maintain proper hydraulic fluid levels and top off with the recommended fluid type as necessary.
- Inspect for Leaks: Check all seals, hoses, and fittings for any signs of leaks. Repair any leaks immediately to maintain pressure and performance.
- Clean the Jack: Regularly clean the jack to prevent dirt and debris from entering the hydraulic system.
- Test the Pressure Relief Valve: Ensure the pressure relief valve functions appropriately to avoid overloading the system.
- Inspect the Ram: Check the cylinder/ram for smooth movement and ensure it retracts properly. Lubricate the ram surface if necessary.
Repair Recommendations
- Seal Replacement: If the jack is leaking, inspect the seals on the piston and replace any worn or damaged.
- Cylinder Repair: If the jack is not lifting correctly, inspect the cylinder for internal damage, scratches, or scoring. Honing or replacing the cylinder may be necessary.
- Pump Issues: If the jack is slow to raise or does not hold pressure, inspect the hydraulic pump and replace any worn components or seals.
- Rod Damage: Inspect the lifting rod for damage and replace it if bent, scratched, or corroded to prevent seal wear and poor operation.
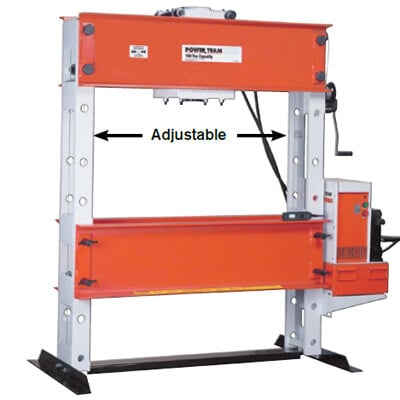

Hydraulic Shop Presses
Preventive Maintenance
- Check Fluid Levels: Ensure the press is topped off with clean, uncontaminated hydraulic fluid.
- Inspect Hydraulic Lines and Fittings: Look for any signs of leaks or wear on hoses and fittings, and tighten connections as necessary.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Regularly grease the press’s moving components (e.g., ram, piston) to ensure smooth operation.
- Inspect the Pressure Relief Valve: Test the pressure relief valve periodically to ensure it functions properly and avoids overloading the system.
- Check Alignment of the Press: Ensure that the press frame, ram, and workpiece holder are aligned correctly to avoid uneven pressure or failure.
Repair Recommendations
- Replace Seals: If the press is leaking fluid, check and replace seals on the ram or cylinder.
- Hydraulic Pump Issues: If the pump is not producing enough pressure, check for air in the system or damaged internal components.
- Check for Structural Damage: If the frame or press components are bent or cracked, they must be repaired or replaced to maintain safety.
- Pressure Adjustment: If the press is not holding or exceeding the set pressure, adjust or replace the pressure relief valve as necessary.

Hydraulic Tools
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic inspections of all hydraulic tools to catch issues early.
- Use Recommended Fluids: Always use the hydraulic fluid recommended by the manufacturer. Using the wrong fluid can lead to premature wear and system failure.
- Avoid Overloading: Never exceed the rated capacity of any hydraulic tool. Overloading can cause serious damage to seals, pumps, and cylinders.
- Storage and Protection: Store tools in a dry, clean environment to prevent rust and contamination. Please keep the tools covered when not in use to prevent debris buildup.
- Proper Training: Ensure all operators are adequately trained in using and maintaining hydraulic tools to prevent misuse and reduce wear.
- By following this guide, you can extend the life of your hydraulic tools, improve their performance, and minimize the need for costly repairs. Always consult the manufacturer’s manual for specific maintenance intervals and recommendations tailored to your tools.

Connect with Our Team
Complete the form and a member of our team will get back to you shortly.
Solution Development
Technical Expertise
Accurate Estimates
On-site Support
Regulatory Guidance
- 1
- 2